NEPTUNE is the farthest planet from the Sun, at an average distance of about 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion km). Neptune is the smallest of the giant planets and is thought to consist of a small rocky core surrounded by a mixture of liquids and gases.

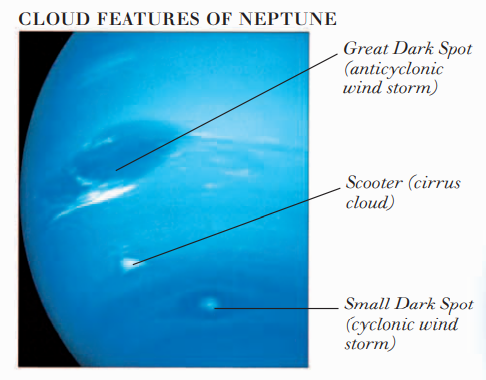
Several transient cloud features have been observed in its atmosphere. The largest of these was the Great Dark Spot, which was as wide as the Earth, the Small Dark Spot, and the Scooter. The Great and Small Dark Spots were huge storms that were swept around the planet by winds of about 1,200 miles (2,000 km) per hour. The Scooter was a large area of the cirrus cloud. Neptune has six tenuous rings and 13 known moons. Triton is the largest Neptunian moon and the coldest object in the solar system, with a temperature of -390°F (-240°C).

Unlike most moons in the solar system, Triton orbits its mother planet in the opposite direction of the planet’s rotation. The region extending out from Neptune’s orbit is populated by Kuiper Belt objects and dwarf planets. They make a doughnut-shaped belt called the Kuiper Belt. The Kuiper Belt objects are a mix of rock and ice, irregular in shape, and less than 600 miles (1,000 km) across. The larger dwarf planets, which include Pluto, are almost round bodies. Pluto was the first object discovered beyond Neptune and was considered a planet until the dwarf planet category was introduced in 2006. It is made of rock and ice and is 1,365 miles (2,274 km) across. It has three known moons. The largest, Charon, is about half Pluto’s size and the two probably had a common origin.









